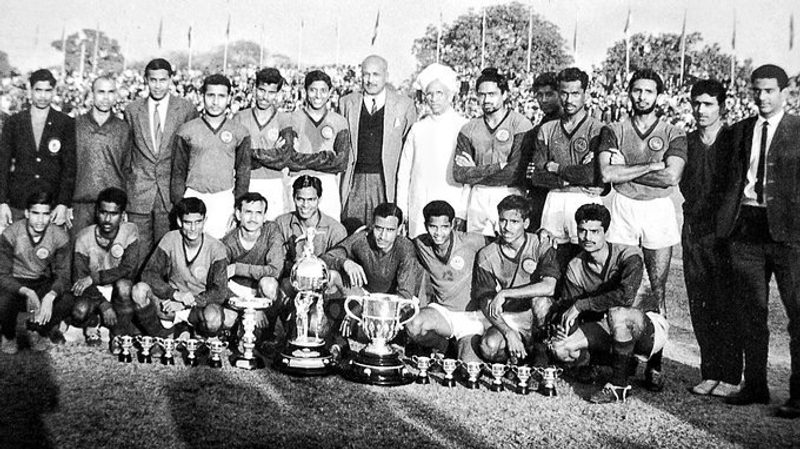
As the oldest football tournament in India, the Durand Cup has been a key contributor to the growth of the sport in the country. More than a century since its inception, the competition continues to be a breeding ground for India’s next generation of footballers.
The Durand Cup is also the oldest football competition in Asia and the third oldest in the world and hence carries with it a rich legacy.
#TuesdayTrivia Durand Cup is the 3rd oldest competition in the world after the Scottish Cup & the @EmiratesFACup pic.twitter.com/bsO5LumQyh
— Shaji Prabhakaran (@Shaji4Football) September 6, 2016
When did the Durand Cup start?
While football was introduced to India by the British troops in the mid-nineteenth century, it gained a much stronger foothold when India’s then Foreign Secretary, Sir Mortimer Durand, founded the Durand Cup in 1888.
Henry Mortimer Durand, the Foreign Secretary of India, started Durand Cup Football tournament at Simla in 1888 pic.twitter.com/d9PPSC66zP
— British India (@BritishRajTimes) May 1, 2015
The competition was held in India and had its first matches played in Dagshai (a canonment in Himachal Pradesh). The tournament’s primary objective was to encourage the importance of health and fitness to the British Indian troops stationed across the country.
Who was the first team to win the Durand Cup?
The first-ever Durand Cup was played between the then-Indian and British army officers, while the final was a Scottish derby between Royal Scots Fusiliers and Highland Light Infantry. The Royal Scots Fusiliers went on to become the first team to win the Durand Cup, with a 2-1 scoreline.
Durand Cup: Before and after Independence
Before India’s Independence, the Durand Cup matches were reserved for the British Indian army. But the competition also welcomed military forces like Provincial frontier, security regiments and other volunteer regiments as participants.
The tournament was suspended in 1914 due to World War I and was revived in 1921. It continued as an All India inter-regiment football competition till 1939 and was held in Shimla. The first 45 years of the tournament saw various English regimental teams assert their dominance but it all changed after 1940.
In 1940, the Durand Committee decided to host the tournament in Delhi. That year, a team from Kolkata, Mohammedan Sporting Club, became the first-ever Indian civilian team to win the competition.
#OnThisDay In 1940 @MohammedanSC became 1st Indian team to win the Durand Cup defeating Royal Warwickshire Regiment. pic.twitter.com/HRO940Io7j
— Hero I-League (@ILeagueOfficial) December 7, 2015
Nearly 50,000 people witnessed history at the Irwin Amphitheatre (now called the Major Dhyan Chand National Stadium). The Kolkata club - which played in a 2-3-5 formation - ended the British monopoly in the Durand Cup.
With goals from forward Hafiz Rashid and left-winger Saboo, the Black Panthers won 2-1 against the mighty Royal Warwickshire Regiment. It was a historic moment.
After Independence, the Durand Cup’s ownership went to the Indian Army, and it remained with them until 2006 when the Osians - an art-house - took over the running and management.
Indian clubs step up in Durand Cup
Now over 130 years old, the Durand Cup has grown from an Army-driven tournament to a competition that actively plays a role in scouting club and national level football talents.
Despite being a homegrown competition, it took 52 years for an Indian club to win the Durand Cup. Mohun Bagan AC, one of the most successful teams in Indian football, was the first civilian team to participate in the competition. However, they didn’t lift the trophy until 1953. Their city rivals Mohammedan SC were the first Indian team to win the Durand Cup in 1940.
The Durand Cup was reinstated in 1950, after it was discontinued from 1941 to 1949 due to World War II, and the competition became fierce to the point where Mohun Bagan and East Bengal kicked off their joint-dominance.
While East Bengal became the first champions of the Durand Cup in the post-Independence era, the Mariners are the only club in the tournament’s history to lift the trophy for three seasons in a row, twice. (1963, 1964, 1965 and 1984,1985,1986).
Mohun Bagan completed Hat-trick of Durand Cup titles (1963-65) as a first non-army club in 1960s. Mohun Bagan beat AP Police(1963),East Bengal(1964) and Punjab Police(1965) in the finals by similar margin of 2-0 to achieve this rare feat.#ThrowBackThursday #MohunBagan pic.twitter.com/XZIxLfAPaN
— Mohun Bagan (@Mohun_Bagan) July 11, 2019
Amidst the Kolkata clubs’ dominance, only two teams have scripted a history of their own in the Durand Cup. In the 1950 edition, where only Indian teams participated, a Hyderabad City Police team captained by legendary Indian player and coach Syed Abdul Rahim handed Mohun Bagan a 0-1 loss in the first post-Independence Durand Cup final.
Between 1950 & 1955 Hyderabad City Police was the strongest team in India. With SA Rahim as coach they won record five consecutive Rovers Cups (1950 -1954) & Durand Cup twice (1951, 1954). City Police players also found success with the national team #indianfootball pic.twitter.com/xlcI8xoDNO
— IndianFootball_History (@IndianfootballH) November 22, 2018
Five years later, the Madras Regimental Centre scripted history as they became the first armed forces side to win the tournament - by defeating Indian Air Force 3-2.
Which is the most prolific team in the Durand Cup?
Mohun Bagan and East Bengal, two teams who have dominated the Durand Cup since the 1950s, jointly hold the record for the most number of titles (16) in the competition’s history.
However, the Border Security Force stands out as the most prolific side in the competition, in terms of the highest win success rate. They have won seven titles and command a win percentage of 77.78 in the finals, while East Bengal, who share the count of 16 titles with Bagan, have registered a win percentage of 61.54.
Teams, rules and format of the Durand Cup
While there is no record of the competition’s format in its earlier days, the Durand Cup is played in two phases - round-robin and knockouts.
A total of 16 teams feature in the group stage round, with four groups consisting of four teams each. Each team is allowed to have a minimum of 22 players and a maximum of 27 to complete their team rosters. As for overseas players’ quota, a team is permitted to have only four players in their team, and they could name only three in their starting line-ups.
After the round-robin schedule, the teams who finish first in their respective groups would progress to the semi-finals stage. Group A’s winner faces Group D’s winner, while Group B’s winner takes on Group C’s.
The Durand Cup, initially a tournament for teams affiliated with the Army, branched out to non-army teams post-Independence. Now, the competition also houses clubs who are associated with the I-League and the Indian Super League.
Feature image courtesy: Twitter/Mohun_Bagan